Starting from our mid-20s, our skin begins a gradual, though consistent, process of aging. The rate of aging is determined by genetic and environmental factors. As known to science today, we cannot influence the genetic factors involved in skin aging. Environmental factors, which include chronic and acute sun exposure, smoke exposure and environmental pollutants, can be prevented by behavioral change or the adoption of healthier lifestyles.
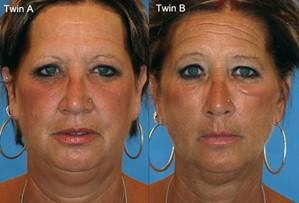
Skin aging is manifested differently in people with different skin tones: while in light-skinned people aging is manifested in the appearance of wrinkles and blemishes, in dark-skinned people the main manifestation of aging is the appearance of uneven pigmentation.
Skin aging in people with different skin tones:

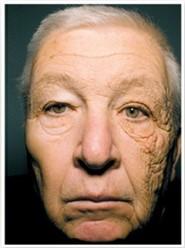
Skin aging is manifested by the loss of its elasticity, the appearance of mimetic wrinkles (called "expression wrinkles") and static wrinkles, sagging of the soft tissue, spots, the appearance of various benign tumors and pre-cancerous and cancerous tumors.
How can skin aging be prevented or delayed?
As mentioned, skin aging is a consistent process and as such cannot be prevented. However, it is also a gradual process – and as such it can certainly be delayed and slowed down.
Protection from solar radiation damage is the first step. This protection should start early in life, preferably in early childhood. Avoiding intentional exposure to radiation (tanning) and protection against unintentional exposure are the cornerstones of being protected. It is now known that almost the entire spectrum of solar radiation accelerates skin aging, but UVA and UVB rays play the major role. Therefore, proper use of sunscreens containing UV filters is an important step in preventing accelerated aging of the skin.
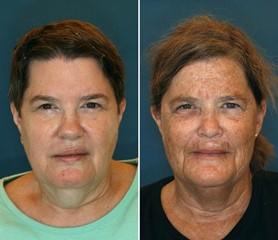
In recent years, several studies have been conducted in groups of identical twins to examine the effect of environmental factors on skin aging. Since these are siblings with the same genetic load (identical twins), these studies make it possible to ignore the genetic factors and isolate the influence of different environmental factors.
These studies have once again reinforced the role of sunlight and smoking on accelerating skin aging.